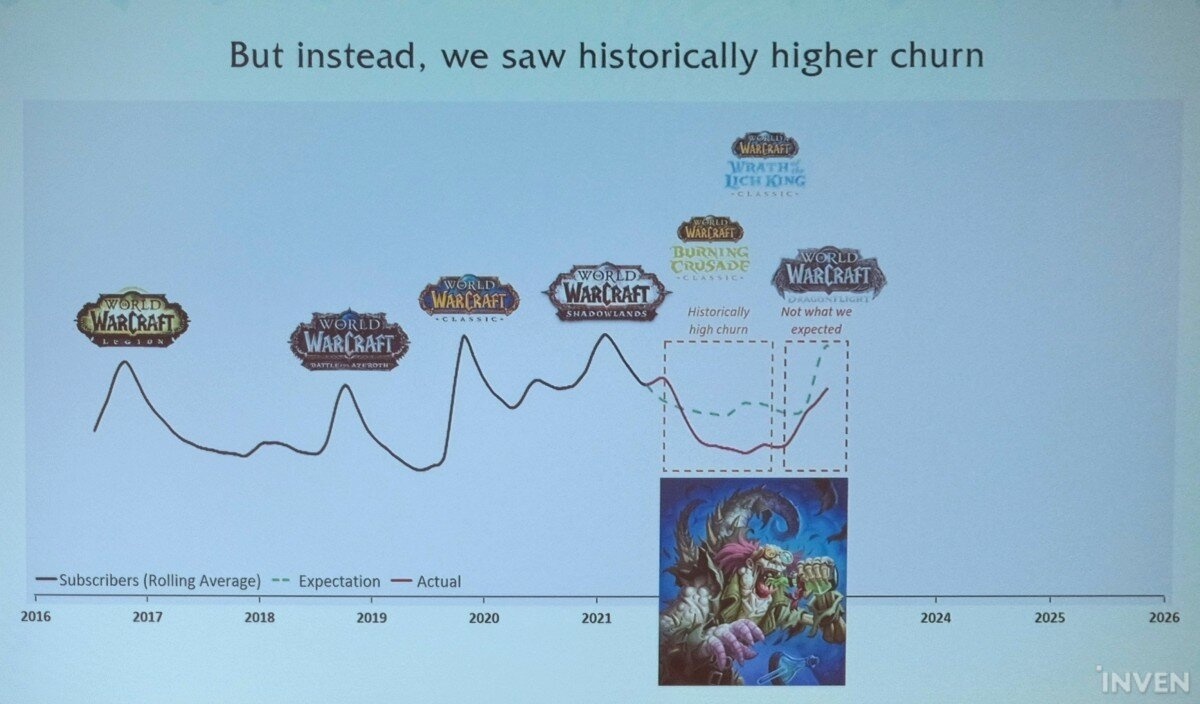
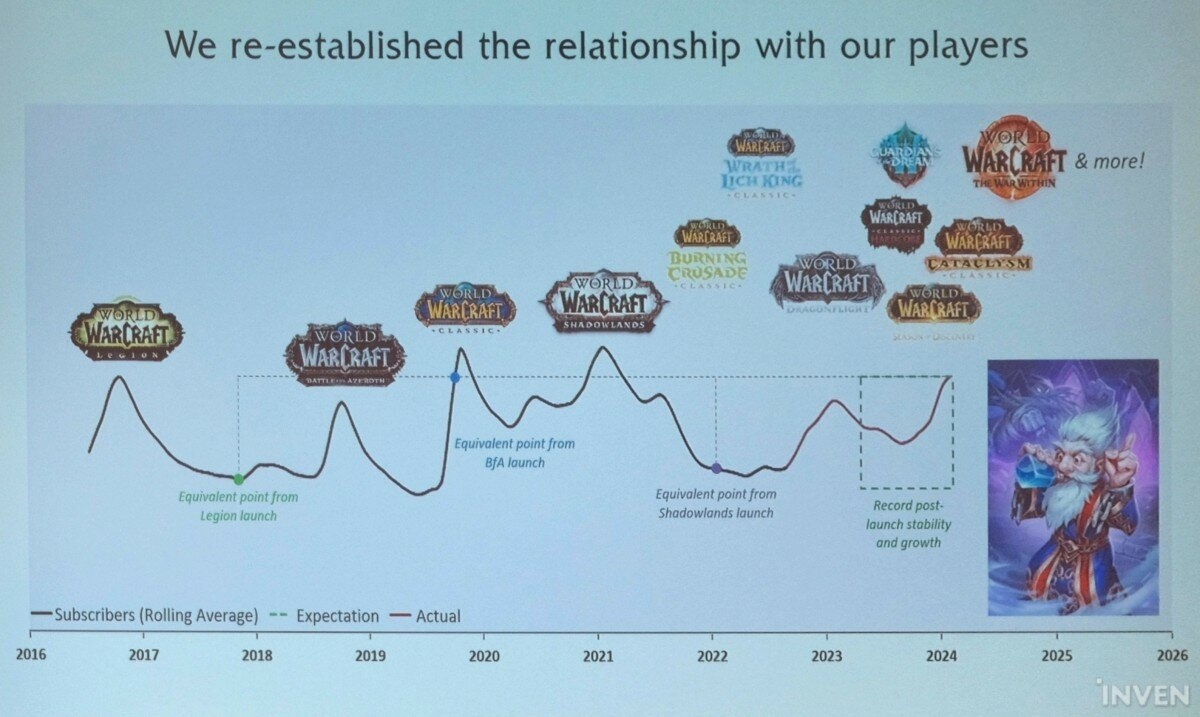
But first, for context, Spencer talked about how things
used to work when budgeting and greenlighting a video game. The Microsoft exec has been producing games for long enough that he can remember when the financials were relatively straightforward. A publisher could set a sales goal (say, 800,000 units), set an earnout goal (how much money they want to make), and set the price of the game (usually $59.99). From there, a video game’s publisher and/or studio could set a budget.
However, the financial calculus has changed. In 2024, most games are sold across multiple storefronts, often steeply discounted mere weeks after release or included as part of subscription services on launch day. Plus, the games themselves take many years to create with the help of hundreds, if not thousands, of team members, sometimes spread across the world. All of this adds up, and as Spencer says, it can cost “$300 million to build a video game.”
Spencer explained how this cost forces three substantial problems: one for all big-budget games, one unique to console exclusives, and one that spans the entire industry.
- The cost “really reduces the risk that publishers are willing to take.” Where previous games needed to sell a few hundred thousand units to justify their cost, new games may need to sell many millions of units. “If you’re a publisher, you know that’s a pretty big number in a world that already has a lot of video games coming.” said Spencer. “How are you going to establish this thing? Am I willing to take the red on new IP — on a new kind of game — when the earnout risk is that high? I think it impinges on the creativity of this industry, which I don’t love. Creativity is like the cornerstone of what we should be about in gaming.”
- This cost is particularly prohibitive for exclusives that can only reach so many players. As Spencer explained in our conversation about the perils of exclusivity and walled-garden consoles, these games need to make additional money to justify the console maker subsidizing the cost of the console. As Spencer explained, “[The case for] exclusivity gets pressured as the cost of the game goes up.”
- According to Spencer, the console market has not grown in the past year. Though Xbox, PlayStation, and Nintendo Switch consoles continue to sell, Spencer notes that many console gamers are simply upgrading — or, to put it another way, they’re not new to the market and won’t contribute to growth. And without new customers, “everybody else’s customer is your success state,” said Spencer. “You can’t succeed unless you draw in customers from other publishers and other platforms. And because you’re not finding new customers with the games that you’re building, everybody’s kind of fighting over the same-size pie.”
These problems have had a very real, substantial, and immediate human cost. The industry has seen consistent and mounting layoffs, including a particularly rough start to this year. Shortly after Microsoft’s acquisition of Activision Blizzard King, the company announced it would be laying off 1,900 workers from its gaming division.
Polygon asked Spencer if the ABK layoffs were part of this wider trend, or if there was something unique about the layoffs as they pertain to the current Xbox business.
“It’s a little bit of both,” said Spencer. “But I’ll say the thing that has me most concerned for the industry is the lack of growth. And when you have an industry that is projected to be smaller next year in terms of players and dollars, and you get a lot of publicly traded companies that are in the industry that have to show their investors growth — because why else does somebody own a share of someone’s stock if it’s not going to grow? —
the side of the business that then gets scrutinized is the cost side. Because if you’re not going to grow the revenue side, then the cost side becomes challenged.