Victoria 3 - Dev Diary #24 - Navies and Admirals
16_9 (5).jpg
The Concept of War and many of the core mechanics presented in
Fronts and Generals, so ensure those are fresh in your mind before reading on!
Your ability to sustain an empire depends, to a large extent, on how well you can compete on the high seas. This is the era of truly global trade, which also meant countries were highly susceptible to disruption of that trade - and the higher they climb, the harder they may fall. In Victoria 3, maintaining a powerful blue-water navy is a large but necessary expense if you wish to ensure the integrity of your markets, overseas colonies, and trade routes during war. And even while at peace, a magnificent fleet can provide your nation with substantial Prestige!
Our design intent for naval gameplay in Victoria 3 is that it should serve as a strategic precision instrument in conflicts between seafaring nations. The sea is not another “front” in a war. The province-based moving Front system works well to represent conflicts over territory but would be nonsensical at sea, where no nation can be said to meaningfully “control” an enormous stretch of ocean. Instead, Admirals and their Flotillas are deployed to meet specific strategic objectives to disrupt the enemy’s military operations or economy, or defend against such attempts by the enemy. A powerful navy can never win you the war on its own, but if deployed correctly under the right circumstances it can be the “ace in the hole” that lets you outsmart even a foe that’s superior on paper.
A clipper departing Luanda in the Portuguese colonial state of North Angola, representing the colony’s connection to the Market Capital in Lisbon.
dd24-1.jpg
dd24-2.jpg
lachek · Nov 17, 2021 at 14:59
" style="box-sizing: border-box; display: inline-block; max-width: 100%; cursor: pointer;">
Convoy Raid and Naval Invasion are
aggressive orders intended to hurt the enemy in different ways, while Intercept and Patrol are defensive orders that counter the other two. But to really understand how these work we have to start by talking about Shipping Lanes and the Supply Network.
Shipping Lanes are facilitated by vessels called Convoys, which are an output of Port buildings. These are created automatically whenever it’s necessary to move goods and/or people overseas. The three main reasons this happens are due to naval Trade Routes between non-adjacent markets, remote States connecting to their Market through a Port, and Battalions sent to frontlines that can only be supplied by ship. When a player is about to take an action that establishes such a shipping lane they are warned of how many new Convoys would be required for this action, which is based on the size of the route or the army supplied.
Shipping Lanes are always established via the shortest possible path, as defined by the number of nodes in the naval network it passes through.
A zoomed-out view of the North Angolan shoreline above, showing the main route ships travel off the coast of southwest Africa. The yellow pin indicates this path is part of Portugal’s Supply Network.
dd24-3.jpg
dd24-4.jpg
lachek · Nov 17, 2021 at 14:59
" style="box-sizing: border-box; display: inline-block; max-width: 100%; cursor: pointer;">

Admirals assigned to Patrol a certain stretch of their Supply Network will eventually be able to detect and engage the raiding navy, causing a naval battle to ensue which will not only sink ships but also send the losing side back to base for repairs for some time. Admirals assigned to Intercept all nodes along a coastline are able to do the same to any raiders along the coast. Convoy Raiding right outside a major entry/exit port, such as in the English Channel, therefore has the chance to seriously disrupt a large number of shipping lanes but also put you at greater risk of detection and interception than if you’re raiding transatlantic shipping lanes on the deep seas. The composition of your navy can also greatly impact how this plays out: a fleet with an accompaniment of Submarines can deal more damage before being intercepted, while a fleet of Monitors has an easier time intercepting raiders but may be more easily sunk if faced down by a more powerful navy.
Because the distance Admirals must patrol plays a difference, there is an inherent asymmetry to Convoy Raiding and Patrol orders. Since a chain is only as strong as its weakest link the damage done to a shipping lane by raiders is the same whether it stretches across 1 node or 10, whereas 10x as many Flotillas are needed to protect the longer route as effectively as the shorter.
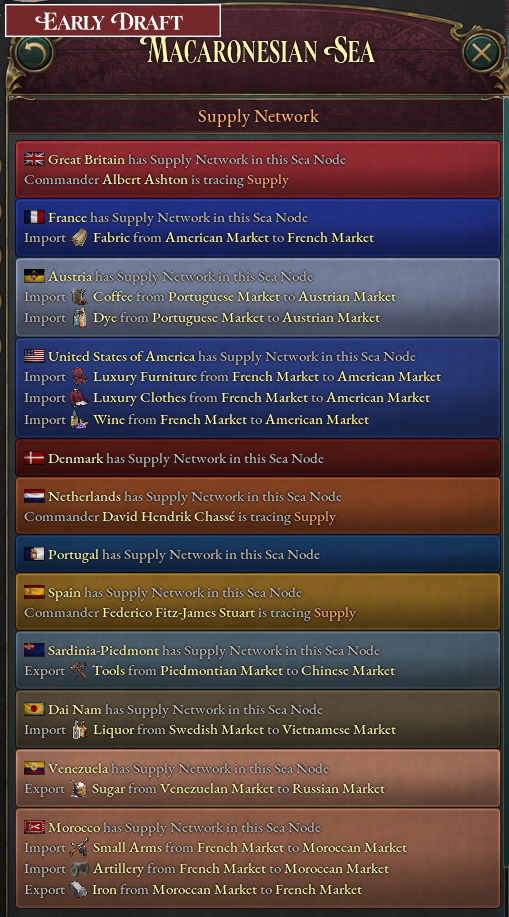
Extremely unfinished breakdown of what is currently happening in the Macaronesian Sea. Look at all those juicy raiding targets!
Naval Invasion is an Order you give to provide naval support for a General’s landing on an enemy coastline. The size of the fleet determines two things: one, how great is the chance that you’ll be able to defeat an opponent’s intercepting fleet, and two, how many Battalions will you be able to successfully land. Even if the enemy has no defensive fleet at all, a naval invasion with a very small fleet might land too weak of an initial force to withstand the enemy’s counter-offense before the rest of the army can arrive. Since Naval Invasion is a one-time Order, once it has been completed it automatically turns into a Patrol Order to protect the shipping lane supplying the new Front.
Concept art of early Ship-of-the-Line and late-game Dreadnought class vessels
dd24-6.jpg
dd24-7.jpg
lachek · Nov 17, 2021 at 14:59
" style="box-sizing: border-box; display: inline-block; max-width: 100%; cursor: pointer;">
Before we wrap up for this week, I want to say a few words about the lack of an order to just “seek out and destroy enemy forces”. In Victoria 3, your commanders - Generals as well as Admirals - are given strategic objectives which they use their manpower and resources to carry out as best they can. If in the process they get into conflict with the enemy’s forces (as they almost certainly will at some point) a battle will ensue. The outcome of that battle determines which direction the war proceeds in. The intent of this is to remove the need to babysit your commanders.
To illustrate this, assume we
did have an order to seek and destroy. The optimal choice would then be to assign this order only to the strongest commander, fight the eventual battle, then revoke this order and give it to another commander while the first one recuperates, and so on.
With an order like “advance front” instead, the General’s intention is simply to capture territory as efficiently as possible, ideally while avoiding enemy interference. If it’s impossible to avoid the enemy, the imperative is to try to be intercepted by as weak of an enemy force as possible. Meanwhile the intent behind “defend front” is the opposite: prevent enemy incursions by defending it in the places where the enemy might advance, bringing to bear as powerful a force as possible. Similarly at sea, “convoy raiding” is about maximizing shipping lane damage while avoiding detection, while “patrol” is about minimizing damage to convoys
by seeking out and destroying those enemy ships attacking them - not to sink ships for its own sake.
Depending on how the war is developing your priorities or overall strategy might certainly shift, causing you to change the orders you’ve assigned or make changes in your ranks to distribute resources differently. But our design intent is that this should only be necessary because your strategy is evolving, not to counter enemy movements or try to minmax your way to victory.
This is an especially important consideration for the naval part of the warfare mechanics. Naval (and aerial) warfare in strategy games commonly face the design challenge of extreme mobility options due to the lack of obstacles to movement. Usually some form of Fog of War and interception-radius mechanics is employed to counteract turtling behavior. The AI also often has to be forced to make mistakes to not become
too good at dodging or intercepting the player in this environment. Even with Victoria 3’s more strategic-level decision making, the freedom of “movement” the sea provides would make a system where being in/avoiding being in the same location as the enemy so as to start/not start a battle extremely micro-heavy, annoying, and highly unfair to either human or AI players depending on implementation.
So instead, in Victoria 3, you tell your Admirals what their overall priorities should be for the war and then they try to do that, using the resources they’ve been allocated, only coming into conflict when they become aware of an enemy Admiral with an order that clashes with their own.
I hope that gives you a good idea of what to expect from the naval mechanics in Victoria 3. Next week we will wrap up this first batch of diaries on the military system by going through the many economic impacts of warfare in Victoria 3. Until then!








![Glory to Codexia! [2012] Codex 2012](/forums/smiles/campaign_tags/campaign_slushfund2012.png)